Why Content Strategy is the Foundation of AI Implementation
Why Content Strategy is the Foundation of AI Implementation
9 min read
![]() Innovatia Guru
:
Jun 21, 2024 2:05:19 PM
Innovatia Guru
:
Jun 21, 2024 2:05:19 PM
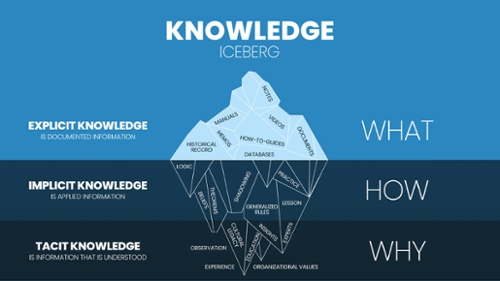
In today's fast-paced digital landscape, businesses are generating and consuming vast amounts of information and knowledge at an unprecedented rate. Hence, they face unprecedented challenges in managing the vastitude of information and knowledge. The ability to effectively manage and leverage this valuable resource has become a critical factor for organizations to stay competitive and drive innovation. This article explores the concept of Information-and-knowledge Management (IKM) and its significance to modern businesses. We will delve into the benefits of IKM, the key components of a successful IKM strategy, challenges to IKM and potential solutions to those challenges, and the evolving trends shaping the future of information-and-knowledge management.
Understanding Information-and-knowledge Management
Information refers to data, facts, and statistics; knowledge represents the understanding, insights, and expertise derived from that information. Information-and-knowledge management involves capturing, organizing, storing, and disseminating information and knowledge within an organization. It utilizes technology, frameworks, and best practices to ensure that information and knowledge are accessible, relevant, and actionable.
The following are the key components of a successful IKM strategy:
Business Benefits of Effective Information-and-Knowledge Management
Implementing robust information-and-knowledge management practices can yield numerous benefits for businesses including:
Information-and-Knowledge Management Component Terms and Definitions
With a better understanding of the importance of information-and-knowledge management, it is worth becoming familiar with the components and terms related to an IKM program.
Enterprise Knowledge Management (EKM)
Enterprise Knowledge Management (EKM) is a holistic approach to managing an organization's knowledge assets. It involves the identification, capture, organization, storage, retrieval, and dissemination of knowledge throughout the enterprise. EKM encompasses both explicit knowledge (formalized and documented) and tacit knowledge (personal insights and expertise). By implementing EKM strategies, businesses can enhance decision-making, promote innovation, and foster collaboration among employees.
Business Information Management (BIM)
Business Information Management (BIM) focuses on the effective and efficient use of information within an organization. BIM encompasses the processes, technologies, and systems employed to capture, store, organize, and distribute information to support business operations. By aligning information management with business goals and objectives, BIM enables organizations to improve productivity, enhance decision-making, and gain a competitive edge.
Information Control
Information control refers to the governance and oversight of information assets within an organization. It involves establishing policies, procedures, and protocols to ensure the integrity, confidentiality, availability, and reliability of information. Effective information control mechanisms protect against data breaches, unauthorized access, and information loss. By implementing robust information control measures, businesses can safeguard their valuable information assets and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements.
ITIL Knowledge Management
ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) is a widely adopted framework for IT service management. ITIL Knowledge Management focuses on capturing, organizing, and sharing knowledge within the IT organization. It involves creating a knowledge base, which serves as a central repository of information, best practices, and lessons learned. By leveraging ITIL Knowledge Management, businesses can improve incident resolution, enhance service quality, and foster continuous improvement within their IT operations.
ITSM Knowledge Management
IT Service Management (ITSM) encompasses the strategies, processes, and practices used to design, deliver, manage, and improve IT services within an organization. ITSM Knowledge Management focuses on capturing, structuring, and sharing knowledge to support the delivery of IT services. It enables service desk personnel and IT teams to access relevant information quickly, troubleshoot effectively, and deliver prompt resolutions to end-users.
Records and Information Management
Records and Information Management (RIM) is the discipline of systematically controlling an organization's records and information throughout its lifecycle. RIM involves activities such as records classification, retention scheduling, storage, retrieval, and disposal. By implementing robust RIM practices, businesses can ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements, mitigate risks, and improve operational efficiency.
Knowledge Mapping
Knowledge mapping involves the visualization and representation of knowledge assets within an organization. It aims to identify key knowledge areas, experts, and gaps in knowledge. By creating knowledge maps, businesses can gain insights into their knowledge landscape, identify areas for improvement, and foster knowledge sharing and collaboration.
Knowledge Silos
Knowledge silos refer to situations where knowledge is isolated within specific individuals, departments, or systems, thus hindering its accessibility and sharing. Silos often arise due to organizational culture, lack of collaboration, or inadequate knowledge management practices. Overcoming knowledge silos requires implementing strategies such as knowledge-sharing platforms, cross-functional collaboration, and fostering a knowledge-sharing culture.
Single-Source Publishing
Single-source publishing is an approach that enables the creation and management of content in a central repository, which can be used to produce various outputs across different channels. By separating content from its presentation format, businesses can efficiently create and distribute content for different formats and platforms such as print, web, mobile, and social media. Single-source publishing streamlines content production, improves consistency, and reduces redundancy.
Challenges in Information-and-Knowledge Management
While the benefits of information-and-knowledge management are significant, organizations also face various challenges in implementing and maintaining effective practices. Some common challenges include:
Overcoming Challenges in Information-and-knowledge Management: Best Practices
While the benefits of effective information-and-knowledge management are significant, organizations often face challenges in implementing and sustaining robust IKM practices. To overcome the challenges and maximize the benefits of IKM, consider the following best practices:
Leadership Support and Strategy Alignment: Strong leadership support is critical for the successful implementation of IKM initiatives. Leaders should champion a knowledge-sharing culture, allocate resources, and promote the value of information and knowledge as strategic assets. Align information-and-knowledge management strategies with overall business goals and objectives. This ensures that knowledge management initiatives are focused on driving value and achieving the desired outcomes.
Employee Engagement: Engaging employees in the IKM process is vital. Encourage collaboration, recognize and reward knowledge-sharing behaviours, and provide training and development opportunities to enhance employees' information-and-knowledge management skills.
Measurement and Continuous Improvement: IKM is an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement and refinement. Establish metrics to measure the impact of IKM efforts. These metrics may include knowledge reuse, reduction in duplication, improved decision-making, and increased innovation. Regularly track and analyze these metrics to evaluate the effectiveness and ROI of IKM initiatives. Gather feedback from users and optimize the knowledge management practices.
Ethical and Legal Compliance: Organizations must adhere to legal and ethical standards when managing information and knowledge. Implement data governance frameworks, ensure compliance with data protection regulations, and establish policies for ethical use and sharing of knowledge.
Robust Governance Framework: Establish clear roles, responsibilities, and processes for information-and-knowledge management. A governance framework helps define accountability, decision-making, and compliance requirements.
Technology Infrastructure: Invest in suitable technologies and tools that facilitate knowledge capture, storage, retrieval, and sharing. Implementing enterprise content management systems, knowledge bases, and collaboration platforms can streamline information-and-knowledge management processes.
Metadata and Tagging: Implement effective metadata and tagging practices to enhance the findability and discoverability of knowledge assets. Properly categorizing and organizing information enables quick and accurate retrieval when needed.
Collaboration, Communication, and Continuous Improvement: Encourage a culture of continuous learning, where employees are motivated to acquire and share knowledge. Foster collaboration and open communication channels to facilitate knowledge-sharing. Encourage cross-functional teams, communities of practice, and mentorship programs to facilitate knowledge exchange and collaboration. Regular assessments and feedback loops help identify gaps and areas for improvement in knowledge management processes.
Evolving Trends in Information-and-knowledge Management
The field of information-and-knowledge management continues to evolve as technology advances. Researchers, visionaries, and futurists foresee the following key trends:
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning technologies are increasingly being utilized to automate and enhance information-and-knowledge management processes. These technologies can assist in data classification, information retrieval, and predictive analytics, enabling more efficient and intelligent knowledge management. Automating processes, extracting insights from unstructured data, and enhancing search capabilities are some key areas where these technologies excel. Intelligent chatbots and virtual assistants are being used to provide instant access to knowledge resources.
Data Analytics and Insights: Organizations are harnessing the power of data analytics to gain insights from their information-and-knowledge assets. Advanced analytics techniques such as text mining and sentiment analysis help extract valuable insights, identify patterns, and make data-driven decisions. These tools enable organizations to derive actionable insights from vast amounts of information. Visualizations, dashboards, and interactive reports make it easier to interpret complex data, facilitating better decision-making.
Collaboration Platforms and Knowledge-Sharing Tools: Collaboration platforms and knowledge sharing tools are evolving to facilitate seamless communication, knowledge exchange, and collaboration among employees. These tools enable real-time collaboration, document sharing, and social interactions, fostering a culture of knowledge exchange and harnessing collective intelligence. Social collaboration platforms, such as enterprise social networks are a great example.
Digital Transformation, Cloud Computing, and Mobility: Digital transformation initiatives and cloud computing technologies are transforming information-and-knowledge management practices. Cloud-based IKM solutions provide organizations with scalable storage, seamless collaboration, and ubiquitous access to information, enabling organizations to store, manage, and share information and knowledge across geographically dispersed teams. Mobility allows employees to access knowledge resources on the go, improving productivity and agility.
Privacy and Data Security: With the proliferation of data breaches and privacy concerns, organizations must prioritize the security and protection of information-and-knowledge assets. Robust cybersecurity measures and data governance frameworks are essential to safeguard sensitive information. Compliance with data protection regulations, data encryption, and secure access controls are crucial considerations.
In today's knowledge-driven economy, effective management and utilization of knowledge have become critical differentiators for businesses. Information-and-knowledge management plays a vital role in enabling organizations to thrive and gain a competitive edge. By implementing a comprehensive IKM strategy—by effectively capturing, organizing, storing, and sharing information and knowledge—businesses can unlock competitive advantages, drive innovation, make informed decisions, enhance operational efficiency, and adapt to rapidly changing market dynamics.
As technology continues to advance, organizations must stay abreast of emerging trends and adopt cutting-edge solutions to effectively manage their information-and-knowledge resources. Embracing the power of IKM will empower businesses to leverage their intellectual capital, make informed decisions, and achieve long-term success in the dynamic business environment of the future. Information-and-knowledge management will remain a cornerstone of success for businesses seeking long-term growth and sustainability.
By leveraging the key IKM practices, organizations can unlock the power of their enterprise intelligence, improve decision-making, enhance collaboration, mitigate risks, drive innovation, and gain a competitive edge in the dynamic knowledge-driven business landscape of the coming decades. Overcoming challenges and adopting best practices are key to unlocking the full potential of information and knowledge within an organization.

Why Content Strategy is the Foundation of AI Implementation
The first step to closing the gaps is to acknowledge that they exist. Streamline your organizational knowledge, making it accessible and actionable...

Changing and evolving terminology can be challenging to stay current with. New terminology is introduced almost daily to try to make sense of the...